Dedicated Bearer setup in LTE and impact on VoLTE Precondition
When a callee has been alerted by the provisional response, the chances of a session establishment failure are minimal assuming network resources are available. So in this case network reservation is the most important and mandatory task.
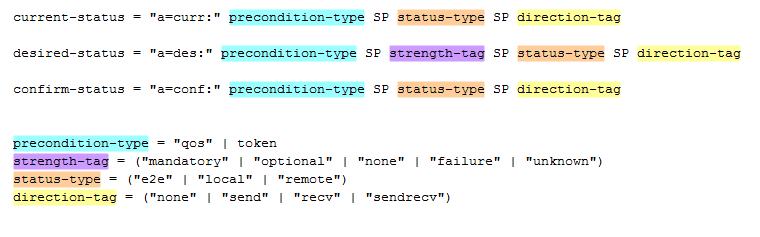
So precondition can be defined as a network resource reservation acknowledgement procedure by which both the terminal users can establish a specific QCI before going to the ringing state. Depending upon the presence of the SDP in the initial INVITE request, desired and local network reservation condition there are several call flows, but we will only consider the primary one.
Suppose UE-A and UE-B are two precondition-enabled VoLTE clients and want to establish a media session between them. Consider UE-A as the initiator of the session.

-
- 1. INVITE
UE-A starts the session by sending an INVITE request(SDP offer) to user B. Within the INVITE request UE-A indicates its capability for precondition by adding the precondition supported header.
Supported: precondition
2. 183/INVITE
Upon receiving the INVITE request, as UE-B is precondition capable, it sends a 183 Session Progress message with the precondition required header and starts exchanging the required QoS parameters.
UE Initiated Dedicated Bearer Setup Request :
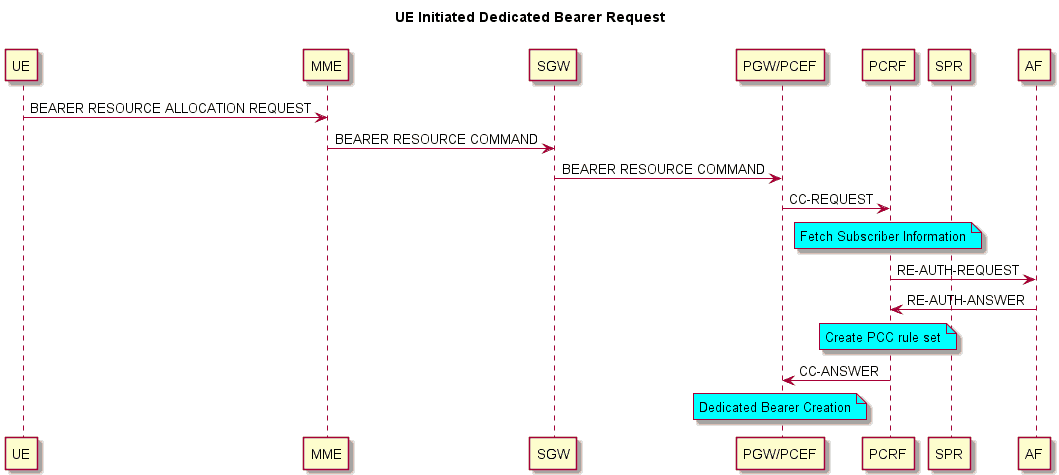
After sending the 183 Session In Progress response UE-B starts reserving the network resources required for this session by sending BEARER RESOURCE ALLOCATION REQUEST to MME. This message contains the QoS class indicator, guaranteed and maximum bit rates for the uplink and downlink, and TFT of UE-A. MME sends this to S-GW as a GTP-C BEARER RESOURCE COMMAND. PCEF now sends a CC-Request to PCRF. PCRF is responsible for checking the subscription status from SPR.
PCRF then invokes a RE-AUTH-REQUEST request to AF. RE-AUTH-ANSWER contains corresponding QoS and charging parameters and PCRF sends this information within CC-ANSWER to PCEF so that it can establish a dedicated bearer. This procedure is called UE-initiated dedicated bearer setup.
Network Initiated Dedicated Bearer Setup Request :

Similarly, after receiving the 183 response by serving P-CSCF of UE-A sends Diameter AA-Request to PCRF indicating mobile using its IP address, and describes the requested media using parameters such as the media type, codec, and port number, and the maximum uplink and downlink data rates. PCRF is responsible for fetching all required subscriber information from SPR and provides the AA-Answer to AF. Then PCRF defines new PCC rules and sends a Re-Auth-Request to PCEF so that it can establish a dedicated bearer. This procedure is called network-initiated dedicated bearer setup.
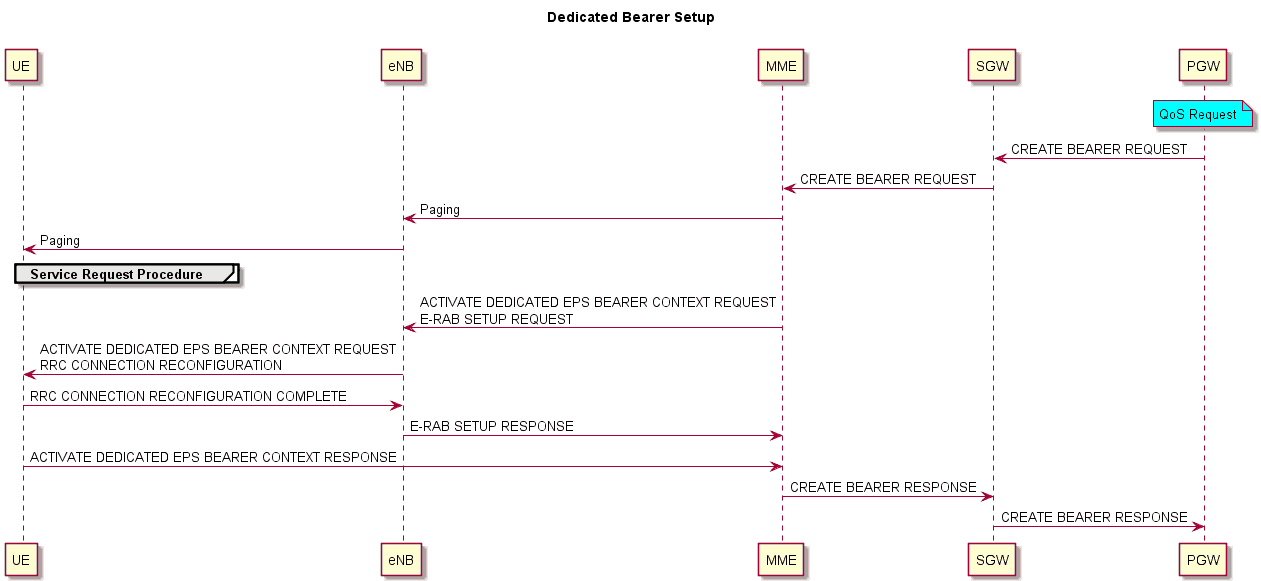
After receiving the new PCC rules from PCRF, P-GW sends QoS parameters and uplinks TEI and TFT for the UE using the CREATE DEDICATED BEARER REQUEST. S-GW forwards this to MME. MME then creates an ACTIVATE DEDICATED EPS BEARER CONTEXT REQUEST with the information received from S-GW, embeds it within S1-AP E-RAB SETUP REQUEST, and forwards it to eNB. After receiving this request from MME, eNB sends an RRC CONNECTION RECONFIGURATION MESSAGE to the UE, which specifies the information received from MME along with the new radio bearer configuration data. The mobile configures the bearer as instructed and acknowledges with an RRC CONNECTION RECONFIGURATION COMPLETE to eNB. eNB now acknowledges with an E-RAB SETUP RESPONSE.
3. PRACK
Parallel to the bearer setup procedure, if the 183/INVITE response contains ‘Require: 100rel’, UE-A issues a PRACK to acknowledge that it received the provisional response containing the SDP body (as well as QoS parameters). Sometimes this PRACK request can also carry the SDP offer but we will ignore that flow for the present.
4. 200/PRACK
Response of PRACK from UE-B. Sometimes this PRACK request can also carry the SDP answer but we will not consider that flow now.
5. UPDATE
After the resource reservation on the UE-A side, the VoLTE client invokes the UPDATE request to acknowledge that the required resource reservation is complete and specifies this within the SDP message body.
After the resource reservation on the UE-A side, the VoLTE client invokes the UPDATE request to acknowledge that the required resource reservation is complete and specifies this within the SDP message body.

6. 200/UPDATE
After receiving the UPDATE by UE-B, if the resource reservation is complete on the MT side, it then acknowledges its status within the 200 OK response.

7. 180 Ringing
After sending the 200OK/UPDATE response, if resource reservation status matches then UE-B sends 180.
8. PRACK
If 180 response contains 100rel then UE-A acknowledges with a PRACK request.
9. 200/PRACK
Response of PRACK from UE-B.
10. 200/INVITE
If the user accepts the call, UE-B sends the 200 OK response of INVITE. As the SDP negotiation is already complete 200OK does not contain the SDP body.
11. ACK
In response to 200OK/INVITE caller acknowledged with ACK.
Reference:
-
- RFC 3312
-
- 3gpp 24.229
- RFC 4032
Author: Arindam Ghosh






